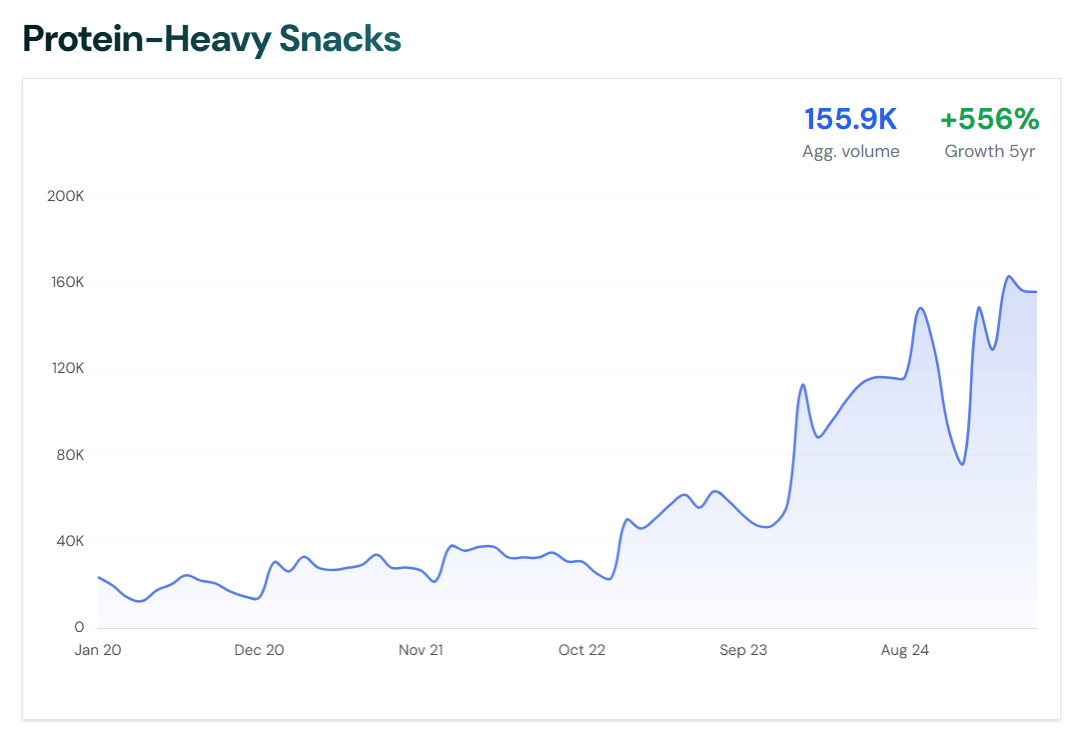
Things are moving faster than ever.
If you’re a business leader, marketer, product manager, or entrepreneur, learning how to identify market trends enables you to stay ahead, make smarter bets, and avoid costly missteps.
In this guide below, we dive deep and get into the nitty gritty details of how to identify market trends.
Let's dive in!
What Are Market Trends?
Market trends are the general direction in which a market or industry is moving over time.
They reflect directional shifts in consumer behavior, technological innovation, economic movements, cultural influences, demographics, and competitive industry dynamics.
Essentially, market trends reflect how the marketplace evolves over time, influencing which products succeed, which marketing strategies are effective, and where investments should be directed.
Some examples include:
- Increasing demand for electric vehicles ( consumer behavior )
- Growth in AI adoption ( technology ) — see our analysis of generative AI trends shaping 2026
- Subscription models replacing one-time purchases ( industry practice )
- Inflation driving value-conscious spending ( economic condition )
Identifying market trends involves analyzing data over time to detect patterns and anticipate future changes.
Trends Vs. Fads Vs. Macro Shifts: Know The Difference
Trends are longer-lasting, more fundamental shifts. They build gradually, gain momentum, and maintain relevance over months or years, influencing business models and consumer expectations.
Market trends represent a profound collective change in what people want, how they behave, and what products or services they value.
Examples of trends:
- Growth in remote work.
- Rising demand for sustainability.
- Shift to subscription services.
- Regulations around data privacy.
If adopted early, trends can help guide product development, opening up a wealth of opportunities.
Fads are short, intense bursts of interest that spike rapidly in popularity but fade quickly, often lasting only a few weeks or months. They are short-lived, with neither long-term substance nor broad market influence.
While fads lack lasting impact, trends have a more enduring effect.
Examples of fads:
- Viral social media challenges.
- NFT profile pictures (2021/2022).
- Meme stocks (e.g., GameStop 2021).
- Novelty products (e.g., galaxy lattes).
Fads carry a high risk - it’s easy to ride the wave, but it’s dangerous for long-term strategy.
Macro shifts (or macro trends) are large-scale, pervasive changes that influence multiple industries or entire economies over more extended periods, often years or decades.
These deeper, large-scale transformations, often generational or structural changes, affect entire economies and societies.
Examples of Macro shifts:
- The move toward circular economies.
- Tech-driven intelligent enterprises.
- Demographic changes (e.g., aging populations).
- Climate change impacts unfolding over decades.
Macro shifts have a very high impact. Organizations that align with macro shifts often future-proof themselves and gain a long-term competitive edge.
Key Takeaway:
Fads are fleeting, trends are strategic, and macro shifts are transformational.
Knowing which is which helps you prioritize what to act on and what to ignore, so you can invest resources wisely, avoid chasing hype, and stay aligned with real, lasting market movements.
Why Identifying Market Trends Is Crucial
Identifying market trends is crucial because it enables businesses and investors to:
- Anticipate demand: Develop products or services aligned with where customers are going, not just where they are. Build what people will want, not just what they want now.
**
Example: Apple anticipated the demand for a device that combined music, phone, and internet, and so the iPhone came to be.
- Avoid disruption: Don’t let competitors outpace you. When trends shift and you’re unprepared, others seize the opportunity.
Example: While Blockbuster failed to recognize the shift toward digital streaming, Netflix pivoted early from DVD rentals to streaming, disrupting the industry.
- Allocate resources smartly: By recognizing where the market is headed, businesses can align their products, services, and marketing efforts with emerging demand.
Example: Unilever invested heavily in sustainable product lines, such as Dove and Seventh Generation, after noticing a growing consumer demand for eco-friendly, socially responsible brands. These brands now grow faster than the rest of Unilever’s portfolio.
- Innovate with purpose: Don’t innovate for novelty, but in response to evolving market needs. Solve real, emerging problems by creating offerings that resonate with future consumers, not just today’s.
Example: Instead of building another gas-powered car, Tesla focused on EVs, responding to growing concerns around climate change, rising fuel prices, and regulation.
- Shape long-term strategy, not just tactics: Long-term direction, not just short-term wins. Go beyond tactics and build future-proof direction.
Example: Microsoft shifted its core strategy to cloud computing (Azure) and subscription services (Office 365), recognizing long-term market movement toward SaaS.
- Stay competitive: By anticipating customer needs and market shifts, companies can innovate and adapt their offerings before they become obsolete.
Example: Nike invested early in direct-to-consumer channels and digital fitness apps, positioning itself ahead of retail trends and gaining a competitive edge when the pandemic struck.
“Trends are the winds that are pushing you along, hitting you in the face, or buffeting you from the side.” ~ McKinsey & Company (2019)
- Adopt relevant marketing & messaging that resonates: Consumer trends shape how brands communicate. Marketers who understand trends can tailor their messaging to align with current values, behaviors, and expectations, thereby enhancing their effectiveness.
Example: Dove responded to cultural shifts around beauty standards by launching its “Real Beauty” campaign. The messaging resonated deeply with consumers tired of unrealistic beauty ideals.
- Find Growth Opportunities: Unlock growth by entering new markets or launching timely products. Trends can open up new markets, customer segments, or product lines, fueling business expansion.
Example: By identifying the trend toward voice assistants and connected homes, Amazon launched Echo and Alexa, entering a new market early and establishing a dominant presence.
- Avoid obsolescence: By adapting before it’s too late. Ignoring emerging trends can lead to decreased relevance and ultimately result in business failure.
Example: Kodak failed to capitalize on the rise of digital photography, despite inventing the digital camera. Its attachment to film led to obsolescence as the market rapidly shifted to digital.
- Enhance business strategy: Through data-driven insights that inform long-term planning.
Example: Spotify uses data and trend analysis to inform product updates, playlist curation, and UX strategy. This trend-driven approach keeps users engaged and strengthens long-term strategic planning.

- Make informed investment decisions: With better timing and market positioning.
Example: Sequoia recognized early signs of a shift toward the gig and sharing economy and invested in Airbnb, well before it was mainstream, leading to massive returns.
Bottom line:
Companies that ignore trends often become reactive, inefficient, or irrelevant.
Understanding market trends is crucial for identifying opportunities early, adapting strategies, and maintaining a competitive advantage in a dynamic business landscape.
This guide will help you understand, spot, validate, and act on real market trends, ensuring your business doesn’t just react to change, but leads it.
Types Of Market Trends
Market trends can be classified in several ways depending on duration , scope , and driving forces .
Understanding the different types helps businesses interpret change more effectively and respond with the right strategy.
Classification By Duration / Scope
- Megatrends / Secular Trends
Megatrends are very long-term trends that occur over decades or even longer.
They represent fundamental, large-scale shifts in economic or market activity, transforming societies, economies, and industries over the course of decades.
Examples: ** The shift from analog to digital technology, & sustainability and the green economy.
“CEOs expect more pressure over the next three years than they experienced over the previous five from technology, climate, and several other megatrends.” ~ PwC (2024)
- Macrotrends
Macrotrends are more specific than megatrends and typically last several years.
They relate to particular sectors or consumer behaviors, and evolve as responses or extensions of megatrends.
Examples: Sustainability-focused products, & remote work adoption.
- Microtrends
Micro trends are smaller, more localized, and shorter-lived movements that typically occur within a specific industry, region, or niche consumer group.
They often emerge from or are a response to a macro trend.
While they may not last as long, microtrends can still present significant opportunities for businesses that are quick to identify and act on them.
Examples: Plant-based meat alternatives (a micro trend in the food industry, stemming from the broader macro trends of health & wellness and sustainability); Short-form Video Content (a trend that has reshaped how businesses connect with younger audiences); & New fashion waves.
- Cyclical Trends
Cyclical trends are long-term, irregular fluctuations that extend beyond a single year, typically several years.
They are driven by the overall state of the economy, following economic cycles such as boom and bust periods (periods of growth and recession). Overall, cyclical trends are influenced by macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and unemployment.
Examples: Real estate market cycles (e.g., A general decrease in construction activity across an industry during an economic downturn); & Business cycles (e.g., Increased consumer spending and production during a period of economic expansion).
- Seasonal Trends
Seasonal trends are regular, periodic patterns in data that recur at regular intervals within the same period each year.
These short-term, predictable patterns are driven by changes in the calendar, such as weather seasons, holidays, or specific events.
Examples: Increased sales of winter coats in the autumn and winter months; Retail sales surge during the holiday season; & Fitness booms in January.
Classification By Market Drivers
- Technological Trends
These are trends triggered by emerging tech innovations related to the development and adoption of new technologies.

Technological trends often lead to the development of entirely new business models or the disruption of existing ones.
Examples: The rise of Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), & Blockchain technology. For a deep dive into current tech trends, see our software development trends for 2026 and generative AI trends.
- Economic Trends
These are trends related to changes in the global or national economy, shaped by international events, shifts in interest rates, inflation, or shifts in consumer spending.
Examples: The growth of the gig economy.
- Political / Regulatory / Policy-Driven Trends
These trends are related to changes in laws, policies, and regulations that impact how businesses operate, such as data privacy laws or trade agreements.
Examples: Shift toward renewable energy due to climate policy.
- Social Trends / Consumer-Driven Trends
These trends reflect shifts in consumer values, attitudes, lifestyle preferences, and behaviors, including the growing demand for corporate social responsibility.
Consumer-driven trends are key to customer loyalty and brand relevance.
Examples: Demand for transparency, ethical sourcing, & Mental wellness.
Practical Steps To Identify Market Trends
Successfully spotting market trends is not about luck; it’s about using repeatable methods supported by real data and examples. You need to collect and analyze data systematically.
Let’s explore the practical steps you can take to identify viable trends, each illustrated with in-depth case studies so you can understand real-world business applications of these trendspotting methods.
“By learning what a trend is, businesses can gain knowledge to improve and build upon existing products and services to gain an edge in their marketplace and even enter into new markets.” ~ Coursera
Step 1: Define Your Research Goals
Before you start, you must define what you’re trying to achieve.
- Are you seeking opportunities to develop a new product?
- Do you want to understand a change in consumer behavior?
- Are you trying to gauge demand for a product in a new market?
Your specific goal will dictate the type of data you collect and how you analyze it.
Example: Coca-Cola sought to understand the decline in soda consumption among health-conscious millennials, which led to the development of low-sugar and functional beverages such as ‘Smartwater+’ and ‘AHA’.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Gather both primary and secondary data to get a comprehensive view of the market.
2.1 Primary Research
Primary research involves collecting new data directly from your customers/target audience.
- Monitor Consumer Behavior: Don’t just listen to what customers say, watch what they do. Track behavioral signals such as usage patterns, feature requests, drop-offs, support tickets, product reviews, or return rates.
These behaviors often highlight unmet needs or evolving preferences long before surveys can do so.
Example: Netflix detected binge-watching behavior and adjusted its content release model for many shows (e.g., releasing full seasons at once), moving away from traditional weekly drops.
- Surveys and Polls: Surveys, interviews, and support logs give you the direct voice of customers.
Use tools like Google Forms or SurveyMonkey to create and distribute surveys to your customer base or a broader target market. Ask questions about their needs, preferences, and pain points.
Example: Amazon continuously uses customer reviews and feedback to optimize its product listings and recommend features (e.g., faster delivery, packaging improvements).
- Focus Groups and Interviews: Conduct in-depth discussions with small groups or individuals. This qualitative method helps you understand the “ why ” behind consumer actions.
Example: Starbucks uses customer surveys to test interest in new flavors or formats before rolling them out, like the plant-based drink options.
- Social Listening: Monitor social media, online communities, and forums for niche conversations related to your industry. Utilize tools like Brandwatch to track trending conversations on platforms like Reddit , TikTok , X (Twitter) , and LinkedIn .
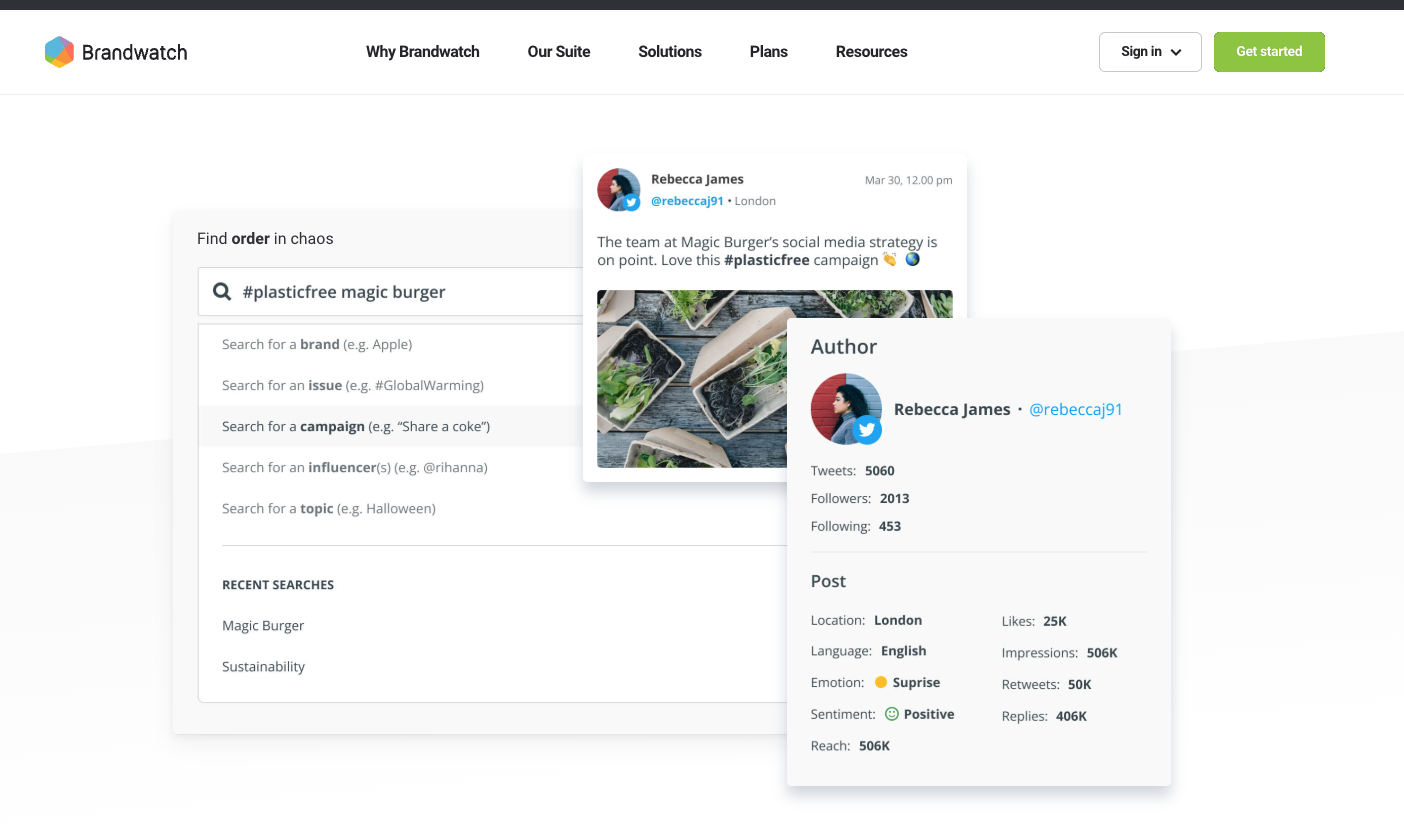
Identify emerging communities or movements (e.g., #zerowaste , #remotework , #no-code ) and pay attention to shifts in sentiment and the frequency of specific topics.
Example: Fenty Beauty partnered with beauty influencers on YouTube and Instagram to meet demand for inclusive makeup shades.
Key Takeaway:
Overall, primary data revolves around closely monitoring customer behavior:
- Track feedback from reviews, support tickets, surveys, and social media.
- Utilize customer journey mapping to identify emerging expectations or pain points.
- Watch for changing purchase patterns (e.g., subscription over one-time sales).
2.2 Secondary Research
Secondary research involves using existing data. It’s often the fastest and most cost-effective way to get started.
- Industry Publications: Read reports, journals, and trade magazines from your industry. These are often excellent sources for spotting emerging trends and market shifts.
Example: IBM regularly applies Gartner insights into AI adoption and cloud computing to evolve its enterprise offerings (e.g., ‘Watson AI services’).
- Study Demographic and Cultural Shifts: Observe generational preferences (e.g., Gen Z’s digital-native behavior or Gen Alpha’s educational tech habits ).
Pay attention to urbanization, migration, remote work, and aging populations - these drive long-term trends. Identify lifestyle changes (e.g., wellness, plant-based eating, minimalism).
Example: Snapchat designed the app’s UX around Gen Z communication habits (ephemeral content, Bitmoji, vertical video).
- Government and Economic Data: Check government sources (such as the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , for instance) for insights into economic indicators, consumer spending, and demographic changes.
Example: Walmart monitored inflation data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics to anticipate shifts in consumer spending, which led to price adjustments and the expansion of private label products. **
- News Outlets: Follow reputable news outlets and business reporters who specialize in your industry.
Example: Netflix tracked entertainment news to spot rising demand for international content, leading to global hits like ‘Squid Game’.
- Competitor Analysis: Conduct a systematic review of your competitors. Analyze their product launches, marketing campaigns, pricing strategies, messaging shifts, and customer reviews. Track M&A activity and strategic partnerships. All these can reveal where the market is headed.
Example: Instagram launched ‘Stories’ after seeing the success of Snapchat’s ephemeral content format.
- Observe What Startups and Innovators Are Doing: Startups often react fastest to shifting customer needs or infrastructure changes.
Utilize platforms like Crunchbase , Product Hunt , or CB Insights to t rack emerging startups in your niche, allowing you to see where capital and experimentation are being invested .
Pay attention to accelerator programs like Y Combinator or Techstars to see which business types are gaining traction. Study what problems new businesses are trying to solve.
Example: Microsoft launched ‘Microsoft Teams’ in response to the rise of Slack and remote work collaboration tools.
- Analyze Technology Adoption: Track not only emerging technologies but also their adoption rate, particularly when they gain traction, such as when infrastructure catches up or when customers start using them in real-world tasks.
Use adoption models (such as the ‘ Technology Adoption Lifecycle ’ ) to assess whether a technology is still niche or is crossing into mainstream. Watch which technologies cross the chasm into real use. Examine infrastructure readiness.
Example: Apple waited to release ‘ARKit’ until smartphone hardware (camera + processors) and developer ecosystems were ready, allowing thousands of AR apps to be created for mainstream use almost immediately.
Step 3: Use Data Analytics
Once you’ve collected data, you need to analyze it to find patterns and trends. Here we go, from signal gathering to interpretation.
- Leverage Existing Business Data: Analyze your own sales figures, website traffic, customer relationship management (CRM) data, customer support logs, feature requests, and usage trends.
Look for patterns in what products are selling, where customers are dropping off in the sales funnel, and which customer segments are most profitable.
Example: Spotify uses streaming data to identify user listening patterns and create curated playlists, as well as recommend new artists.
Utilize Analytics Tools: To identify search trends and online interest.
Rising Trends : This commercial tool utilizes a database of over 12,000 curated trending topics, products, and keywords to help you identify under-the-radar trends before they become mainstream.
It can provide insights into emerging consumer problems and niche markets with growth potential.
Example: HubSpot creates blog content and tools centered on the most frequently searched business questions, enhancing their SEO authority and product relevance.
- Google Trends : Track search interest in specific keywords and topics over time and across different locations. This free tool is excellent for gauging public awareness and comparing the popularity of various products or ideas. For more advanced Google Trends techniques and Google Trends alternatives, check out our comprehensive guide.
Example: Etsy merchants use search trends to adjust product offerings seasonally (e.g., DIY Halloween kits, Christmas ornaments, or back-to-school items). Learn more about using Google Trends for market research to uncover profitable opportunities.
- SEO Tools: Use tools like Semrush or Ahrefs to analyze competitor performance, identify rising keywords, and find content gaps.
Example: Glossier leveraged rising search interest in skincare ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid and niacinamide, to inform product development.
- Predictive Analytics: For a more advanced approach, use predictive analytics and machine learning to forecast future trends based on historical data.
Example: Amazon uses predictive analytics to forecast what products will be in demand, enabling highly accurate inventory planning and personalized recommendations.
“In the dynamic landscape of modern business, predictive analytics has emerged as a critical tool that enables more accurate forecasting of market trends, revenue streams, costs, and potential risks, significantly enhancing strategic planning.” ~ FP&A Trends (2025)
- Test and Validate Trends Internally: Run small experiments (e.g., landing pages, pilot features, A/B testing) to validate market interest. Use Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) to test trend-driven ideas and collect real user data before making significant investments.
Example: Airbnb initially tested short-term rentals through simple MVP listings before becoming a global platform.
Key Takeaway:
The bottom line of search analytics is so that you can:
- Identify increasing interest in keywords relevant to your industry.
- Look for seasonal patterns or consistent upward movement in specific topics.
- Compare regional or global interest levels to detect early-stage adoption.
Step 4: Stay Connected To The Market
Identifying trends is an ongoing process. You must continually monitor the market and be prepared to adapt.
- Attend Industry Events: Participate in conferences, trade shows, and seminars (virtual or in-person) to stay informed about innovations and connect with thought leaders. Take notes on recurring themes or buzzwords - these are often trend indicators. Network with frontline professionals who are witnessing change in real-time.
Overall, these events are excellent for networking with experts, seeing new technologies firsthand, and hearing about emerging ideas.
Example: Canva has grown, in part, by attending design and edtech conferences, listening to educator needs, and adapting features accordingly.
- Follow Industry Reports: Read annual or quarterly reports from firms like McKinsey , Deloitte , Gartner , or IBISWorld .
Example: Patagonia actively follows sustainability research to stay ahead of eco-friendly apparel trends and material innovations.
- Engage with Experts & Thought Leaders: Tune in to what respected voices in your industry and adjacent fields are saying, through newsletters, webinars, podcasts, and forums. Look for ideas that recur across sectors, not just one-off opinions.
Example: Notion collaborates with productivity influencers and thought leaders to align product features with emerging trends in remote work and digital organization.
- Monitor Regulatory & Policy Shifts: Track proposed or upcoming regulations that affect your industry, such as those related to sustainability, data privacy, and labor laws.
These are often leading indicators of forced market change, especially important in finance, energy, health, education, and tech. Governments typically shape trends through legislation (e.g., data privacy, sustainability, ESG investing , carbon regulation).
Example: Unilever adjusted sourcing and production strategies to align with EU sustainability regulations and carbon footprint goals.
- Regularly Review Your Analysis: Make a habit of revisiting your market analysis regularly (e.g., quarterly or annually) to ensure your business strategy aligns with the most current market conditions.
Ideally, make trendspotting a habit by:
- Scheduling monthly or quarterly trend review meetings.
- Maintaining a shared trend-tracking document across your team.
- Assigning someone to own trend identification and insights as part of their role.
Example: Shopify adjusts its product strategy quarterly in response to evolving e-commerce needs and merchant feedback.
Key takeaway:
As far as staying connected to the market goes:
- Read annual or quarterly industry reports from reputable sources.
- Subscribe to trade magazines or industry newsletters .
- Follow LinkedIn influencers, podcasts, and blogs in your industry.
- Track competitors with BuzzSumo or Semrush alerts .
- Make trendspotting a habit.
High-Value Strategies For Trendspotting
These high-value trendspotting strategies go beyond surface-level observation, helping you consistently identify, validate, and act on meaningful business trends.
- Use Multiple Data Sources: Combining many sources reduces bias, reveals converging signals, and increases confidence.
Example: Nike used a combination of customer feedback, social listening, industry research, influencer content, and retail data to launch ‘Nike FlyEase’ and expand inclusive product lines, including adaptive apparel.
- Triangulate Signals Across Industries: Don’t just look within your own industry - study adjacent or completely different sectors to spot transferable trends.
Example: Fintech companies borrowed gamification mechanics from mobile gaming to improve user engagement (e.g., Robinhood’s interface ) .
Example: Etsy monitors niche DIY and crafting trends on Pinterest to forecast demand and guide seller recommendations.
- Map Trends to Human Needs (Jobs-To-Be-Done): Identify whether a trend addresses a functional, emotional, or social customer need. Trends with straightforward human utility are more likely to stick.
Example: The rise of ‘meal kits’ (e.g., HelloFresh) wasn’t about food; it addressed time-saving and decision fatigue (functional + emotional needs).
- Avoid Jumping In Too Early Or Too Late: Use industry reports, Google Trends, or adoption benchmarks to determine if a trend is in its early, growth, or maturity stages and time your entry accordingly.
Example: NFC (Near Field Communication) existed for years but had low merchant and consumer adoption. Apple waited to launch Apple Pay until contactless payment tech and consumer trust were widespread. They entered just as mobile payments were gaining mainstream adoption.
- Look for “Cultural Collisions”: Pay attention when multiple macro trends collide, that’s often where new market opportunities emerge.
Example: Peloton emerged at the intersection of wellness, connected fitness, and remote work - a perfect storm of converging cultural shifts.
- Analyze Ecosystem Growth, Not Just Product Popularity: A trend becomes sustainable when it supports an ecosystem - developers, service providers, creators, and brands around it.
Example: The rise of the creator economy was validated when platforms like YouTube, Patreon, and TikTok built monetization ecosystems for creators.
- Observe Behavior, Not Just Buzz: Prioritize what people consistently do over what they say or share. Use analytics, sales data, retention metrics, and repeat usage to validate whether a trend has sticking power.
Example: YouTube saw high engagement with creator “how-to” and “reaction” content, leading to the development of “YouTube Shorts” and enhanced creator monetization tools.
- Prototype Around Trends Quickly: Don’t just spot trends - test them with low-risk experiments like MVPs, landing pages, or pilot features.
Example: Dropbox famously tested demand with a short explainer video before building the whole product - a fast validation of growing interest in cloud storage.
- Combine Qualitative & Quantitative Inputs: Blend data (search trends, sales, user behavior) with observable cultural insights (interviews, online conversations, field notes) for a more complete view.
Example: LEGO saw a rise in adult purchases through sales data, then engaged directly with online AFOL (Adult Fans of LEGO) communities to co-create kits tailored to the interests of grown-ups.
Common Pitfalls To Avoid When It Comes To Market Trends
Error 1: Mistaking viral hype or media attention for a sustainable trend.
Just because something is viral doesn’t mean it’s sustainable.
Fix: Look for behavioral adoption, not just buzz. Trends that solve real problems tend to last longer than fads.
Error 2: Jumping in too early or too late.
Entering before the market is ready = no adoption. Entering too late = saturated market.
Fix: Use adoption curves, Google Trends, and industry reports to determine the optimal timing.
Error 3: Chasing every new trend instead of strategic alignment.
Just because a trend exists doesn’t mean your company can or should chase it. Forcing a trend into your strategy when it doesn’t align can backfire.
Fix: Validate whether the trend aligns with your customers’ needs , brand , and capabilities .
Error 4: Chasing competitors instead of customers.
Copying what competitors do without understanding why, leads to a reactive strategy.
Fix: Focus on your customers’ pain points and behaviors, not just industry moves.
Error 5: Ignoring counter-trends or backlash.
Every trend creates a countertrend (e.g., social media detox, privacy-first tools).
Fix: Stay alert to backlash, fatigue, or shifts in sentiment around popular movements. Monitor for early signs of resistance or ethical concerns.
Error 6: Over-relying or acting on intuition or anecdote without supporting data.
This creates blind spots and bias.
Fix: Cross-verify trends with customer behavior, search trends, expert reports, and real-world activity.
Error 7: Assuming global trends = local relevance
What’s trending globally may not translate to your market or audience.
Fix: Always localize and validate trends with your target segment and region .
Error 8: Using non-representative data.
Relying on feedback from just one demographic (e.g., Gen Z, urban users) skews insights.
Fix: Ensure your data sources reflect your whole customer base and target market .
Error 9: Failing to monitor trends continuously.
Trends evolve. What worked last year may be irrelevant now.
Fix: Build a regular trend-tracking process and cadence (e.g., quarterly reviews) to monitor, validate, and adapt accordingly.
Trend Validation Checklist
Here’s a robust checklist/framework to evaluate whether a trend is worth your time, resources, or strategic pivot. Use this checklist to assess whether a trend is worth acting on.
1. Is the Trend Backed by Behavioral Data?
◻ Are people doing something new (not just talking about it)?
◻ Can you see measurable shifts in user behavior, sales, or adoption?
◻ Are there repeatable patterns, not just one-time spikes?
2. Is There Evidence Across Multiple Data Sources?
◻ Do search volumes ( Google Trends , AnswerThePublic , etc.) confirm rising interest?
◻ Are industry reports or analyst forecasts highlighting it?
◻ Are startups, influencers, or media covering the trend (engagement metrics)?
◻ Are you seeing real-world business activity (funding, hiring, new products, sales data)?
3. Is the Trend Gaining Momentum - or Peaking?
◻ Is the trend in the early growth or mainstream stage (not oversaturated)?
◻ Are adoption curves and benchmarks pointing up?
◻ Are more companies/investors entering the space recently?
4. Does the Trend Align with Customer Needs or Pain Points?
◻ Does the trend solve a real, clearly identified customer problem?
◻ Have customers requested or responded positively to related features, products, or content?
◻ Does it align with known emotional, functional, or social needs (Jobs-To-Be-Done)?
5. Have You Tested the Trend in a Low-Risk Way?
◻ Have you run small pilots, MVPs, or landing page tests?
◻ Did you gather clear signals (sign-ups, conversions, engagement)?
◻ Are early results promising enough to justify scaling?
6. Is the Infrastructure or Ecosystem Ready?
◻ Are the tools, platforms, or technology required to act on the trend mature enough?
◻ Are consumers/clients equipped to adopt it (e.g., hardware, internet access, knowledge)?
◻ Is regulation or policy supporting or accelerating this trend?
7. Can Your Business Realistically Act on the Trend?
◻ Do you have the capabilities (skills, tech, time) to respond quickly?
◻ Does it fit your brand, mission, or customer base?
◻ Can you enter or differentiate in this trend space without stretching too far?
8. Are You Distinguishing Trend from Fad?
◻ Is the trend tied to deeper societal, economic, or technological shifts?
◻ Does it have cross-industry relevance or staying power?
◻ Is there a consistent trajectory (not just viral moments)?
Final Sanity Check
◻ Are you validating with both quantitative data (metrics, sales, trends) and qualitative insights (feedback, interviews, sentiment)?
◻ Are you prioritizing long-term relevance over hype?
◻ Have you defined what success looks like if you act on this trend?
◻ Have you considered the negative or unintended side effects (ethical, environmental, social) of acting on the trend?
Use a scorecard approach whereby trends that tick over 60% of the boxes are worth exploring further. You can set a threshold for which trends to pursue Vs. Monitor Vs. Discard.
Tools to Help You Spot Trends Faster
While strategic thinking and observation are key, the right tools can significantly accelerate the process of identifying and validating market trends.
Here are a few high-impact resources worth adding to your toolkit:
- Trendwatching alternatives
Modern trend research platforms that help identify emerging consumer behaviors and market shifts.
Best for: Professional trend research and industry insights.
- Rising Trends
Tracks fast-moving trends across TikTok, Google, Reddit, and X (Twitter). Great for spotting early cultural signals and validating emerging interest.
Best for: Real-time cultural insight and early trend discovery.
- Exploding Topics alternatives
Trend discovery tools that identify topics before they become mainstream.
Best for: Finding emerging trends and niche opportunities.
- Google Trends
Shows how search interest in a topic changes over time and by region. Helpful in validating seasonal spikes, regional demand, and long-term search patterns.
Best for: Tracking search behavior and regional interest.
- AnswerThePublic
Visualizes questions people are asking about a keyword or topic. Helps uncover customer intent and content gaps.
Best for: Understanding how consumers perceive and discuss trends.
- Trend Hunter alternatives
Comprehensive trend analysis platforms for spotting cultural and consumer trends.
Best for: Cultural trend analysis and consumer behavior insights.
- Crunchbase
Tracks startups, funding rounds, and acquisitions. A great way to spot early innovation signals and investment-backed market bets.
Best for: Monitoring emerging business models and sectors.
Pro Tip: No single tool gives you the full picture. The best trendspotters combine multiple sources - search data, startup activity, consumer behavior, and cultural sentiment - to validate what’s real and actionable.
For instance, you can use Rising Trends alongside AnswerThePublic to cross-check what people are searching for against what they’re talking about and sharing online.
Tool Spotlight: Rising Trends
In a fast-moving digital landscape, capturing trends early is a competitive edge, but it’s challenging to track everything happening across platforms in real-time.
That’s where Rising Trends comes in handy.
Rising Trends is a specialized trend discovery platform that blends data-driven metrics with human curation and niche discovery to help you spot high-potential under‑the‑radar trends before they go mainstream.
It reveals what people are actually engaging with, not just what’s being discussed in headlines.
This tool filters out hype, highlights niche products and behavioral shifts, and offers early access to breakout apps and market niches, making it an effective combo of qualitative + quantitative insights.
Why Rising Trends Is Useful:
- Tracks multiple platforms in one place.
Pulls data from sources like TikTok , Google , Reddit , and X (Twitter) , saving time and giving you a more holistic view of what’s gaining traction across different audiences and ecosystems.
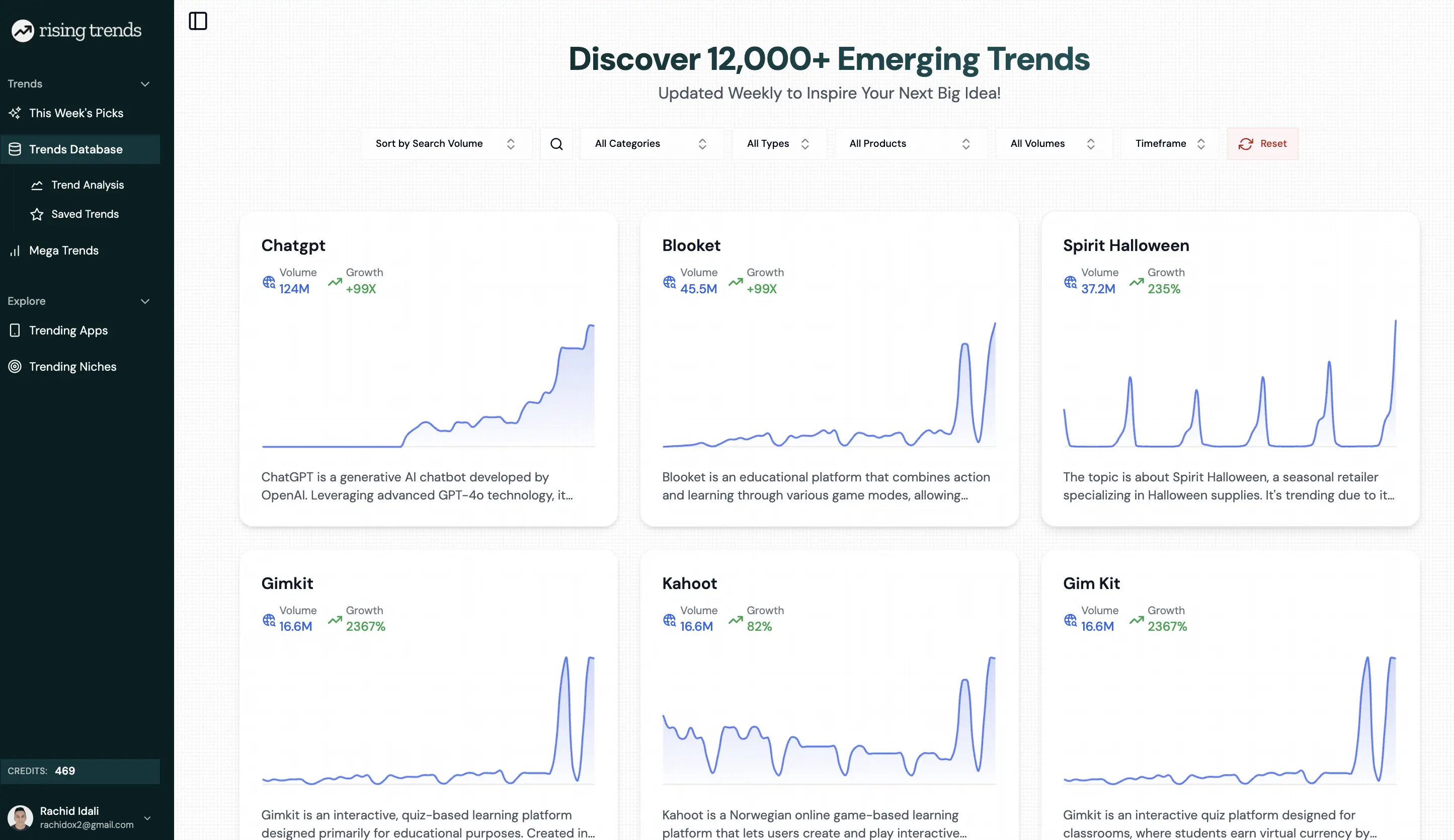
Focuses on emerging signals, not just popularity.
Unlike tools that show what’s already mainstream, Rising Trends helps you spot what’s just beginning to take off, allowing you to act before the market gets crowded.Great for early trend validation.
If you’ve identified a potential trend through customer behavior or industry insights, you can use Rising Trends to cross-check whether public interest is growing in real time.Fills the cultural insight gap.
While tools like Google Trends show search behavior, Rising Trends surfaces what people are reacting to emotionally and culturally, providing more context around why something is trending.Useful for content and product timing.
You can use Rising Trends to: time your campaigns with rising interest; spot content opportunities before others do; and identify feature ideas based on honest conversations and sentiment.Helps spot cross-industry trends.
Since Rising Trends is not limited to one vertical, you can spot patterns or themes (e.g., sustainability, AI tools, creator economy) that may be emerging in adjacent industries, and apply them to your own.Supports agile, real-time strategy.
Unlike static trend reports, Rising Trends updates frequently, making it ideal for teams that work in short sprints and need real-time insights to stay relevant.
Use Cases For Rising Trends
Whether you’re building products, planning content, or shaping strategy, Rising Trends helps you move from a gut feeling to data-backed insight, quickly.
Here are some practical, high-impact use cases on how you can leverage trend awareness to gain a strategic advantage, using the Rising Trends platform.
- Early product or feature ideation.
Use the platform to discover emerging problems, desires, or themes gaining attention before they are incorporated into mainstream product roadmaps.
Example: A SaaS team notices a spike in AI workflow hacks trending on Rising Trends and validates demand for an AI-powered feature in their app.
- Validate trend signals you’ve spotted elsewhere.
Use Rising Trends to cross-check intuition, customer feedback, or competitor moves against real-time public interest across multiple platforms.
Example: A DTC brand sees customers mentioning a niche wellness ingredient and confirms it’s trending on Rising Trends.
- Inform content strategy & campaign timing.
Use the platform to create content around rising topics while competition is still low, or time campaigns with cultural moments.
Example: A marketing team sees a niche aesthetic rising on Rising Trends and tailors their ad visuals and hashtags to match before it peaks.
- Discover cross-industry inspiration
Use Rising Trends to spot trends from other industries that could inspire innovation on your own.
Example: A retail brand notices a growing interest in gamified learning and explores applying this concept to loyalty rewards.
- Refine target audience messaging.
Use it to understand what your audience is currently engaging with online so you can align tone, cultural references, and creative direction to match current sentiment.
Example: A health & wellness brand targeting Gen Z updates its TikTok ad script and visuals after noticing a spike in interest around “silent walking” and “girl dinner” on Rising Trends - tapping into familiar concepts that resonate with their audience’s current mindset.
- Stay ahead of competitors in fast-moving niches.
Utilize the platform to identify niche trends before your competitors, particularly in industries such as fashion, wellness, AI, or consumer technology.
Example: A consumer tech startup spots “AI note-taking” gaining traction on Rising Trends. Within weeks, they launch a lightweight Chrome extension that addresses this need, capturing early users before major players react.
- Support Testing & Validation of New Ideas
Use it to justify internal experiments, MVPs, or pilot campaigns by showing real-world momentum for related trends.
Example: A startup founder planning a plant-based snack launch uses Rising Trends to demonstrate rising online interest in sustainable eating and “zero-waste snacks.” This data helps secure additional funding by proving market timing and consumer demand.
Final Thoughts
Identifying market trends isn’t just about following the latest buzz. It’s a strategic discipline that combines data, observation, and cultural insight.
By systematically monitoring customer behavior, leveraging diverse data sources, validating signals with tools like Rising Trends, and balancing qualitative with quantitative inputs, businesses can anticipate shifts before they become mainstream.
The key is to remain curious but cautious: avoid rushing into every “hot” trend. Instead, apply rigorous validation and align trends with your unique goals and audience needs.
Actionable Recommendations to Get Started:
- Set clear research goals: Define what you want to learn or achieve before diving into trend data.
- Establish a multi-source monitoring routine: Regularly combine customer feedback, search data, social listening, and competitor analysis to gain a comprehensive understanding of the market.
- Leverage tools like Rising Trends: Utilize real-time trend tracking to validate early signals and gain insight into cultural context.
- Test ideas quickly: Launch small experiments or pilot programs to see how trends resonate with your audience.
- Collaborate and share insights: Make trendspotting a team effort by holding regular check-ins and using a shared dashboard or document.
- Review and refine quarterly: Trends evolve, so revisit your process and adapt as needed to stay relevant.
In a rapidly evolving market, your ability to spot and act on the right trends early will differentiate your brand, drive innovation, and unlock new growth opportunities.
See trend analysis in action: Check out our data-backed deep dives into 7 software development trends for 2026 and 7 generative AI trends for 2026 — real examples of how to identify and validate emerging market trends using the methods outlined in this guide.
Health & Wellness Trend Reports: For industry-specific trend analysis, explore our programmatic trend pages powered by real search data: fitness trends 2026 (50+ trends in recovery, hydration, and functional training), haircare trends 2026 (from rice water to scalp health), and sleep trends 2026 (the booming sleep economy from supplements to grounding sheets).